Ultrafiltration vs Reverse Osmosis
If you’re trying to decide between ultrafiltration vs reverse osmosis, the two most common membrane water treatment methods, this guide can help. Both methods are effective at removing most contaminants from water, but they differ in their approach. In general, reverse osmosis (RO) is more reliable and durable than ultrafiltration (UF), which is why it is used more in industrial settings such as municipal treatment plants, seawater desalination plants, or commercial bottling plants. Still, both methods have their advantages. Which is the most appropriate for you?
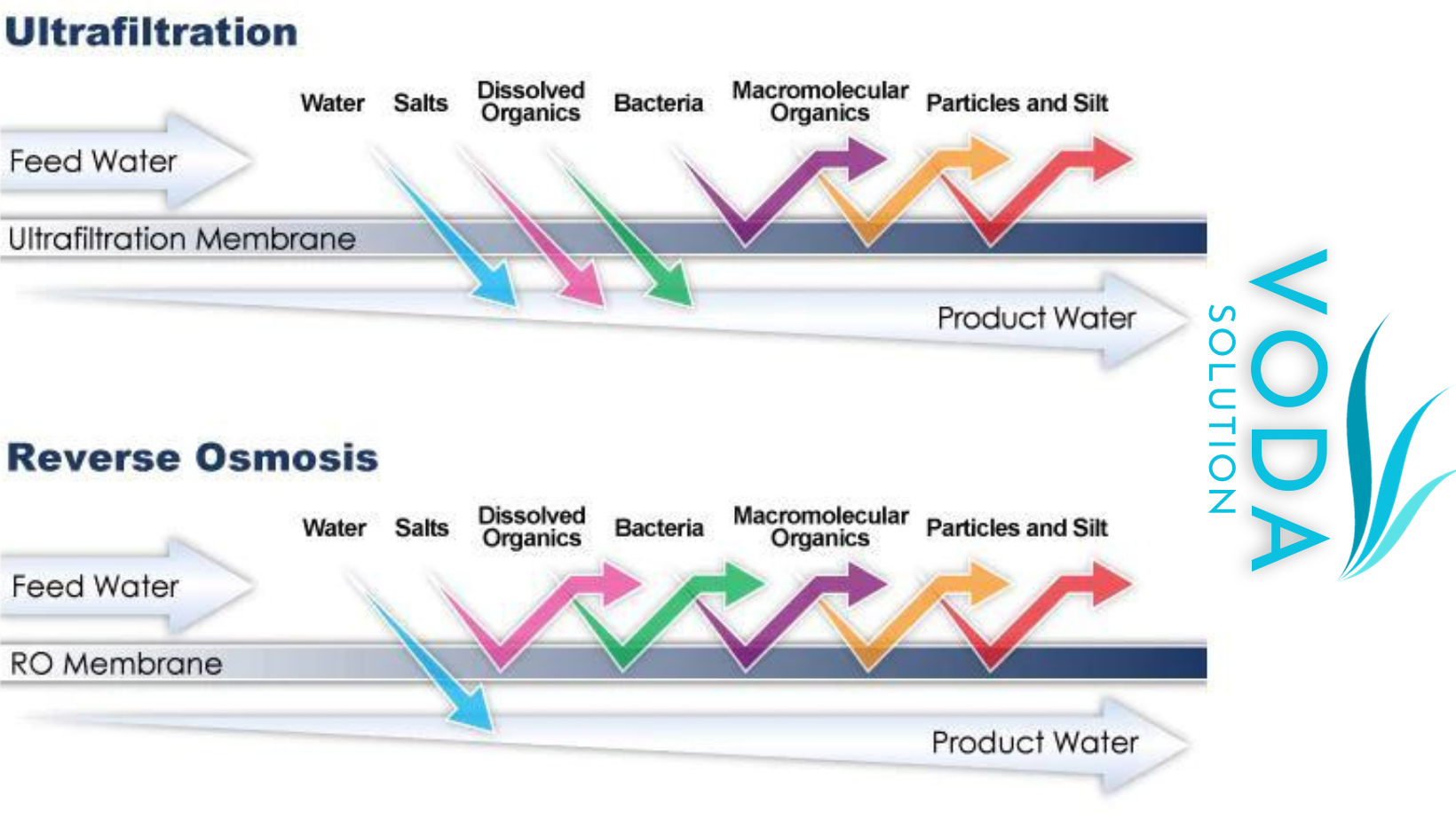
Ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis are two methods for removing impurities from water. Both use pressure to force water through a membrane.
Ultrafiltration is more commonly used in industrial applications because it is more economical than reverse osmosis and can treat large volumes of liquid and in less time. It also doesn’t require as much energy or maintenance as reverse osmosis systems, making them ideal for remote locations where electricity is unreliable or not available in large quantities (such as oil rigs).
What are the differences between water treatment by ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis ?
Ultrafiltration is a membrane filtration process that removes particles, microorganisms and turbidity from water, while reverse osmosis is a purification process, removing the smallest molecules present in the water.
Ultrafiltration could be the pretreatment to feed water to reverse osmosis .
The first stage of an ultrafiltration system uses pressure to force liquid through the tiny pores of the ceramic membranes, which are so small that they filter out bacteria and viruses, as well as other organic materials such as organic solids and microorganisms (such as bacteria). In the second stage, more pressure is applied to further filter out any remaining large particles or molecules before passing them through another set of ceramic membranes with smaller pores than those used in the first stage. This removes even more contaminants from your drinking water source, such as heavy metals that occur naturally in some groundwater sources; such as wells or boreholes drilled into granite rock formations called aquifers which can lead to health problems if consumed long term without proper treatment systems.
What elements does ultrafiltration remove from water ?
In the ultrafiltration process, the membrane has an approximate pore diameter of 0.01µm to 0.1 μm (microns). This pore size allows separating particle sizes of different nature (suspended solids, fine particles, colloids, algae and microorganisms such as bacteria) within the range 0.04 and 0.1 μm (microns).
- Ultrafiltration is used to remove bacteria and viruses from drinking water.
- Ultrafiltration is used to remove dissolved solids.
- Ultrafiltration is used to remove turbidity. Ultrafiltration is also used to remove flavors and odors, which are carried by water molecules (such as chlorine).
What elements does reverse osmosis remove from water?
Reverse osmosis membrane element pore sizes can range from 0.1 to 5,000 nanometers (nm) depending on the application . The pores in the membrane are small enough to restrict the smaller molecules present in the water such as minerals and salts.
Reverse osmosis removes high levels of dissolved solids, including:
- These include bacteria and viruses that can cause disease in humans.
- Pesticides and herbicides, which are found in most municipal water sources due to runoff from nearby agricultural areas. These chemicals can be harmful if ingested in large doses over time (even though they are technically considered “safe” by the EPA). They can also contaminate groundwater and reach tap water through this process.
- Heavy metals such as lead, copper and mercury, all known neurotoxins that have been linked to various health problems, including cancer, as well as neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease or Parkinson’s disease, if consumed during long periods of time at sufficiently high concentrations.
What maintenance does an ultrafiltration membrane require?
- Periodic cleaning (ultrafiltration systems include a self-cleaning or backwash system).
- Periodic tests.
- System maintenance (e.g. replacement of filters and pumps).
The lifespan of an ultrafiltration membrane can vary depending on several factors, such as water quality and proper maintenance.
What maintenance does a reverse osmosis membrane require?
Reverse osmosis membranes are very durable and can last between 3 and 5 years. The membrane does not need to be replaced unless it is worn or damaged, but you should clean it regularly with special reverse osmosis membrane products. Eliminate biological growth, carbonate scale, silica, etc.
Replace the reverse osmosis membrane every 3-5 years to ensure maximum performance, especially if you live in an area where there is hard water or if you use the system frequently (e.g. daily).
Applications ultrafiltration can be used
Ultrafiltration is used for water treatment. Ultrafiltration technology is also used in the food and beverage industry, pharmaceutical industry, and oil and gas industries.
- Gray water treatment (without fats).
- Reuse of non-waste industrial water.
- Eliminate suspended particles and turbidity in drinking water.
- Retention of bacteria and viruses in drinking water treatment.
- Seawater pretreatment before reverse osmosis in desalination.
- Protein concentration (enzymes, dairy proteins, egg whites) in the food industry.
- Clarification and stabilization of fruit juices and wines (elimination of turbidity components).
- Eliminate cellular waste and bacteria in beer production.
- Eliminate polysaccharides, proteins and colloidal impurities in sugar refining.
- Sterile filtration in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry.
- Recovery and concentration of metals in the mining industry.
- Treatment of effluents and wastewater in various industries.
Applications of reverse osmosis.
Reverse osmosis is used to remove dissolved solids and other contaminants from water. The process consists of passing water through a semipermeable membrane that only allows the passage of molecules smaller than those of interest. Reverse osmosis can also be used to concentrate minerals, such as salt or sodium chloride (NaCl).
- Selective separation and purification in industrial processes.
- Pre-concentration of milk and whey in the dairy industry.
- Dealcoholization of alcoholic beverages.
- Desalination of seawater to obtain drinking water.
- Elimination of chemical and biological contaminants in the treatment of drinking water.
- Reduction of total dissolved solids (TDS) and suspended particles in water.
- Treatment of water contaminated with industrial chemicals before discharge into the environment.
- Recovery and reuse of water in industrial processes, reducing the demand for fresh water.
Reverse osmosis is used in several industries, including:
- Food and beverage processing
- In the food industry it helps purify water without adding chemicals or altering the taste or appearance. It is ideal for removing impurities from dairy products, juices and teas; ensure that drinks do not contain bacteria or mold spores; remove pesticides from fruit juices; reduce the sodium content in canned soups; prevent spoilage by killing microorganisms during storage periods prior to bottling/packaging operations.
- Pharmaceuticals – Reverse osmosis removes many organic compounds found in raw materials used by pharmaceutical companies so they can make safe products free of harmful contaminants.
- Water treatment for products whose main ingredient is ultrapure water.
- Seawater desalination.
Both ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis are effective methods for treating water; Depending on your situation, you may need one or the other.
Both ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis are effective methods for treating water. If you are looking to remove particles from water in large volumes , ultrafiltration is a great option; It is also useful if you want to remove dissolved solids. Reverse osmosis is an excellent option if you need to remove dissolved solids from drinking water to meet a higher quality standard, but it has some disadvantages compared to other types of filtration systems (such as higher energy costs).
Conclusion
In conclusion, both ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis are effective methods for treating water; Depending on your situation, you may need one or the other.